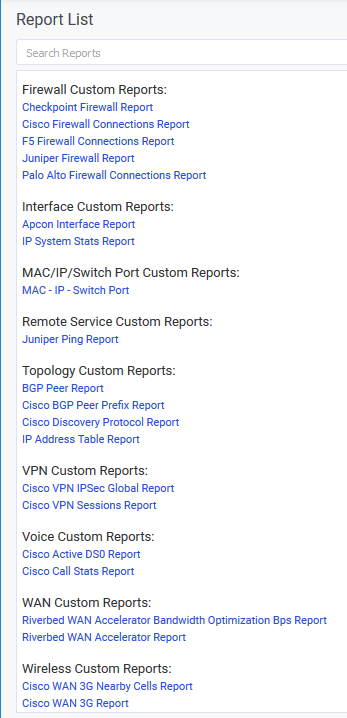
Index
- Overview
- Installing a CDT Package
- Manage Data Type Polling
- Automatic Entity Removal
- Reporting on CDTs
Overview
Custom Data Types (CDTs) are data description packages provided by Statseeker that can be used to:
- Extend the types of devices that can be polled by Statseeker
- Extend the data that can be collected by Statseeker's polling process
CDTs are created by Statseeker in response to advances in technology, making:
- New devices network-aware
- Enhancements to existing network aware devices, resulting in a wider range of data/metrics being made available for collection and analysis
As a customer, you can request a CDT package to suit your requirements, and Statseeker will work with you to provide a package with the ability to poll the device, return the data, and provide the reporting functionality to make use of the custom data. For further details, see Requesting a Custom Data Type (CDT) Package
Installing a CDT Package
In order to install a previously downloaded CDT package:
- Select Administration Tool > Statseeker Custom Services > Manage Packages
- Click Choose File, browse to your previously downloaded CDT package, select it, and click Open
- Click Upload
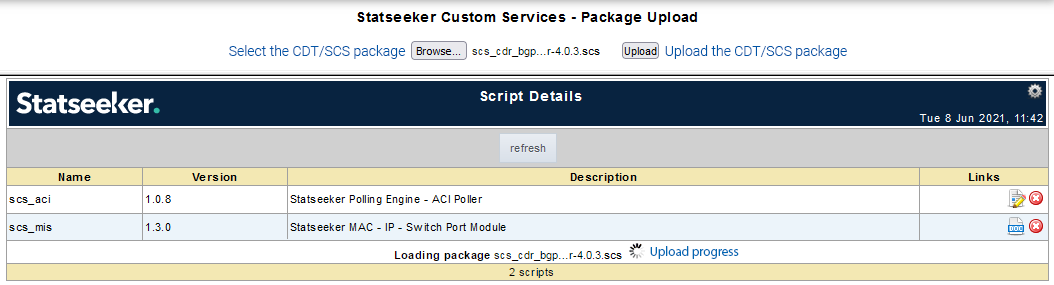
- Click Details to review the upload process results
Once the upload process is complete, a summary of the result is displayed.
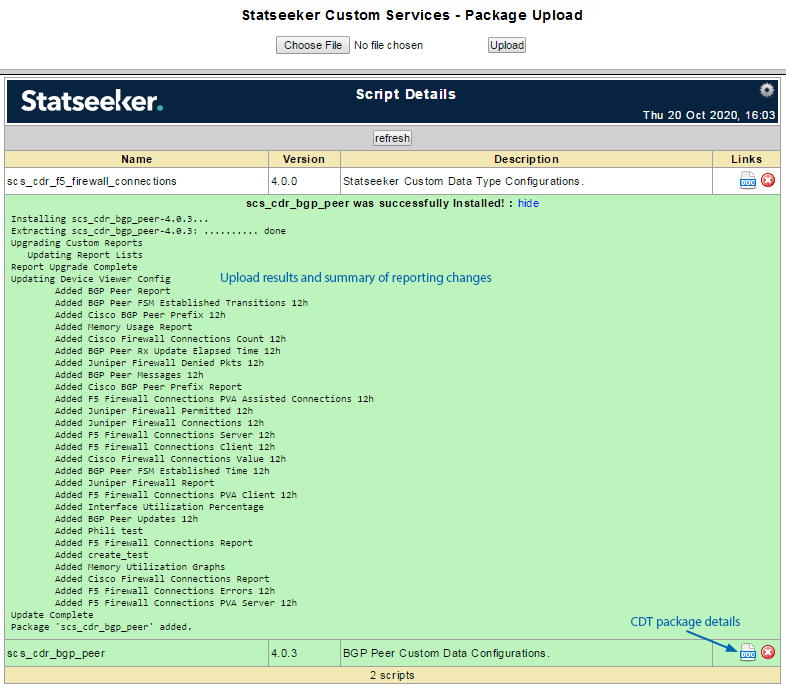
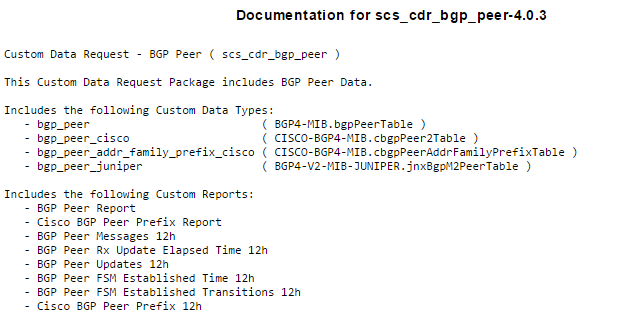
- Successfully uploaded CDT packages offer a document link providing information on the package contents
Manage Data Type Polling
Once a CDT package has been installed, you will need to enable polling for that new data type. The Custom Data Ranges page provides the ability to restrict polling of both default and custom data types to defined IP address ranges or to disable polling entirely.
- Go to Administration Tool > Network Discovery > Custom Data Ranges to display the associated configuration page
- Click Edit (top-right) to enable configuration
- Locate the newly added data type and set the Status to On
- The data collection Status for a given data type can be toggled On or Off per type, vendor within that type, and product within that vendor
- Click Save
By default, Statseeker will query all interfaces on your network for any custom data type that has been enabled, so it is recommended that ranges be assigned for these data types to assist in keeping within licensed entity limits.
To assign a discovery range for a custom data type:
- Go to Administration Tool > Network Discovery > Custom Data Ranges to display the associated configuration page
- Click Edit (top-right) to enable configuration
- Rules to include/exclude multiple data ranges can be assigned at any exposed data type level in the following formats:
include/exclude NetworkAddress[/Netmask] or NetworkPattern
- Additional include/exclude ranges may be added/removed by clicking the +/- buttons
- Click Save
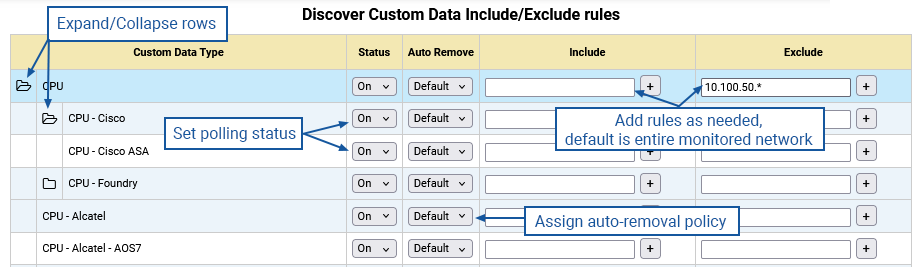
- Child categories within a custom data type (e.g., vendor, vendor/product, etc.) will inherit the assigned ranges of their parents and require their own rules to edit these ranges as needed
- The include/exclude IP ranges specified for a CDT type must be a subset of those in the IP Address Scan Ranges or Hosts File entries
Automatic Entity Removal
By default, when a device stops reporting an object/entity of a given type, that entity is flagged as disabled, and polling for that specific entity is disabled. This means that old entities are excluded from reports to prevent them from polluting the data, but their historical data is kept for reference, or in the event that the entity comes back online.
Automatic Entity Removal is a method to clean up SNMP entities that are no longer found. If Auto Removal = on, the entity will be deleted instead of flagged as disabled. By default, Auto Removal is set to off for all entity types, with the exception of interfaces.
Auto Removal:
- Does NOT come into effect when a device is unreachable or a port is not responding
- Only comes into effect when a device configuration changes and the device itself reports that the entity no longer exists
For CDTs that feature parent-child relationships (CPU, Memory, Temperature, etc.), the child CDT will inherit the Auto Remove behavior from the parent unless specifically configured otherwise.
Manual Entity Removal
In addition to Statseeker's Automatic Entity Removal policies, entities can be manually deleted or flagged as disabled. Manually managing SNMP entities is achieved through the Manage Devices interface. See SNMP Entity Management for details.
Reporting on CDTs
The CDT packages contain customized reports that are available once the package has been installed. These reports can be accessed from both the Console and Reporting panels, grouped by their technology type.